Electrophysiological studies
23 May 2021 / 4:26 pm
What is it ?
Electrophysiological studies are an electrical study of the heart’s conducting system. EPS is particularly useful for some patients with heart rhythm disturbances and symptoms of palpitation.
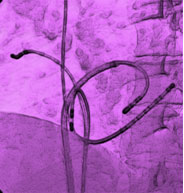
How is it performed ?
You will need to lie flat on a special bed. Flexible electrodes are passed up into the heart from the vein at the top of your leg. Local anaesthetic is injected to minimise any discomfort. Under x-ray guidance the electrodes are positioned to identify any abnormal nerves or pathways within the heart. Sometime the heart is stimulated to beat quickly to help this process. Once an abnormality is detected, high frequency energy can be delivered from the electrode tip to burn it away in a procedure called “ablation”.
How long does it take ?
Usually 1 to 2 hours however more complex procedures such as ablation for atrial fibrillation can take many hours.
Are there any risks ?
The main risks of the procedure are bleeding or bruising at the top of the leg. There is a risk of blood accumulating around the heart. If ablation is required there is a small (1% or less) risk of damage to the heart’s normal conducting system such that you end up requiring a pacemaker.
What happens next ?
You will be asked to lie flat for a few hours after the procedure. You should not drive for a few days.